##什么是JDBC? JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的java API。可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用java语言编写的类和接口组成。
##JDBC原理
JDBC通过标准(一系列接口)定义了访问数据库的通用API,不同的数据库厂商根据各自数据库的特点提供的对JDBC的实现(实现类包)。
图示:
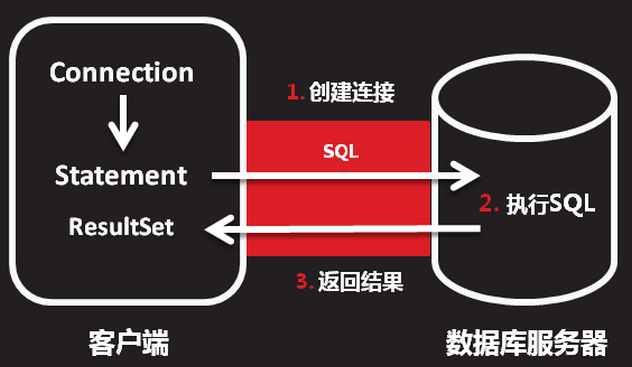
##核心API
// 1.装载 OracleDriver 到内存里,
// 通过static块实现在DriverManager中的“自动注册”
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver");
// 2.创建Connection的实现对象,
// 根据url连接参数找到与之匹配的Driver对象,调用其方法获取连接
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.10.205:1521:tarena";
String username = "jsd1303";
String pwd = "jsd1303";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, pwd);
// 3.通过Statement对象,传送SQL语句
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 4.执行SQL并获得结果集
// 执行select语句
ResultSet rs = stmt
.executeQuery("select id,real_name,create_date from nova_account");
// 执行update、insert、delete语句
// stmt.executeUpdate("");
// 遍历结果集
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String realName = rs.getString("real_name");
Date createDate = rs.getDate("create_date");
System.out.println("id: " + id + " real_name: " + realName
+ " create_date: " + createDate);
}
// 5.关闭资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
##DAO Data Access Object,数据访问对象,用于应用程序与数据源进行交互。
##Statement隐患
- 用Statement操作时,代码的可读性和可维护性差
- Statement操作sql语句每执行一次都要对传入的语句编译一次,效率比较差
- 存在sql注入风险
##PreparedStatement ###说明 预编译的Statement
- 创建PreparedStatement时需要SQL语句参数。此SQL语句可包含0到多个IN参数,每个IN参数用一个问号(“?”)作为占位符。每个问号的值在该语句执行前,通过适当的setXXX方法来提高
- PreparedStatement对象对包含的SQL语句已预编译,所以其执行速度快于Statement对象。
- PreparedStatement使用预编译语句,sql中传入的参数不会和原来的语句发生任何匹配关系,有效防止SQL注入。
###核心API
//pstmt对象将包含的SQL语句发送给DBMS,并为执行作好准备
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement("UPDATE tableName SET m = ? WHERE x = ?");
//给占位符进行赋值
pstmt.setLong(1,12345);
pstmt.setInt(2,100);
//执行SQL语句
pstmt.executeUpdate();
//pstmt.execute();
//pstmt.executeQuery();
##事务控制 ###事务特性ACID
- 原子性(atomic):事务必须是原子工作单元,对数据修改,要么全都执行,要么全都不执行
- 一致性(consistent):事务在完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态
- 隔离性(insulation):由并发事务所作的修改必须与任何其他并发事务所作的修改隔离
- 永久性(duration):事务完成之后,对系统的影响是永久性的。
###相关API
//关闭事务的自动提交 conn.setAutoCommit(false); //提交事务 conn.commit(); //回滚事务 conn.rollback();
##JDBC批处理 ###优点
- 降低应用程序和数据库之间的网络调用
- 相比单条SQL,批处理是更高效
- 能有效降低对Oracle的负载
###API
- addBatch(String):Statement类的方法,多次调用该方法可以将多条sql语句添加到Statement对象的命令列表中
- addBatch():PreparedStatement类的方法,多次调用该方法可以将多条预编译的sql语句添加到PreparedStatement对象的命令列表中。
- executeBatch():把Statement对象或PreparedStatement对象命令列表中的所有sql语句发送给数据库进行处理。
- clearBatch():清空当前sql命令列表。
###例子
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
try{
con = getConnection();
String sql = "insert into service(id,account_id) values(?,?)";
con.setAutoCommit(false);
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
int count = 0;
int batchSize = 1000;
for(Service : Services){
stmt.setString(1,Service.id);
stmt.setString(2,Service.accountId);
stmt.addBatch();
if(++count >= batchSize){
stmt.executeBatch();
}
}
stmt.executeBatch();
stmt.close();
con.commit();
}catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
con.rollback();
}finally{
if(con!=null){
try{
con.close();
}catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
##getConnection优化 ###ThreadLocal原理 用于实现线程内的数据共享,即对于相同的程序代码,多个模块在同一个线程中运行时要共享一份数据,而在另外线程中运行时又共享另外一份数据。
###ThreadLocal核心API
private static ThreadLocallocalCon = new ThreadLocal (); protected static synchronized Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{ Connection con = localCon.get(); if(con == null){ con = openConnection(); localCon.set(con); } return con; } </pre> ##BaseDAO封装 public class BaseDAO { private ThreadLocallocalConn; /** * 获得连接 * * @return * @throws SQLException */ protected synchronized Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = localConn.get(); if (conn == null) { conn = DBUtils.getConnection(); localConn.set(conn); } return conn; } /** * 开始事务 */ public void beginTx() { Connection conn; try { conn = getConnection(); conn.setAutoCommit(false); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 提交事务 */ public void commitTx() { Connection conn; try { conn = getConnection(); conn.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 回滚事务 */ public void rollbackTx() { Connection conn; try { conn = getConnection(); conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 关闭连接 */ public void closeConnection() { Connection conn = localConn.get(); try { if (conn != null) { conn.close(); localConn.set(null); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } </pre> ##分页查询 ###Oracle分页参数 //说明 //currentPage -- 当前页 //numPerPage -- 每页几条 //querySql -- 查询语句 //记录总数 int totalRows = 0;//TODO 查询得到符合条件的记录总数 //总页数 int totalPages = totalRows % numPerPage == 0 ? totalRows / numPerPage : (totalRows / numPerPage + 1); //开始记录的位置 int startIndex = (currentPage - 1) * numPerPage; //最后一条记录的位置 int lastIndex = currentPage == totalPages ? totalRows : (startIndex+numPerPage); //分页sql StringBuffer pagingSql = new StringBuffer(); pagingSql.append("select * from ( select my_table.*,rownum as my_rownum from ( "); pagingSql.append(querySql); pagingSql.append(" ) my_table where rownum <= ").append(lastIndex); pagingSql.append(") where my_rownum > ").append(startIndex);###MySQL分页select * from tablename limit start,pageSize;